Bridging patient's expectations and clinical outcomes
Clinicians make complex decisions every day, often guided by experience and personal preferences. Simultaneously, patients struggle to understand treatment options, creating a gap between expectations and outcomes and often resulting in post-treatment dissatisfaction.
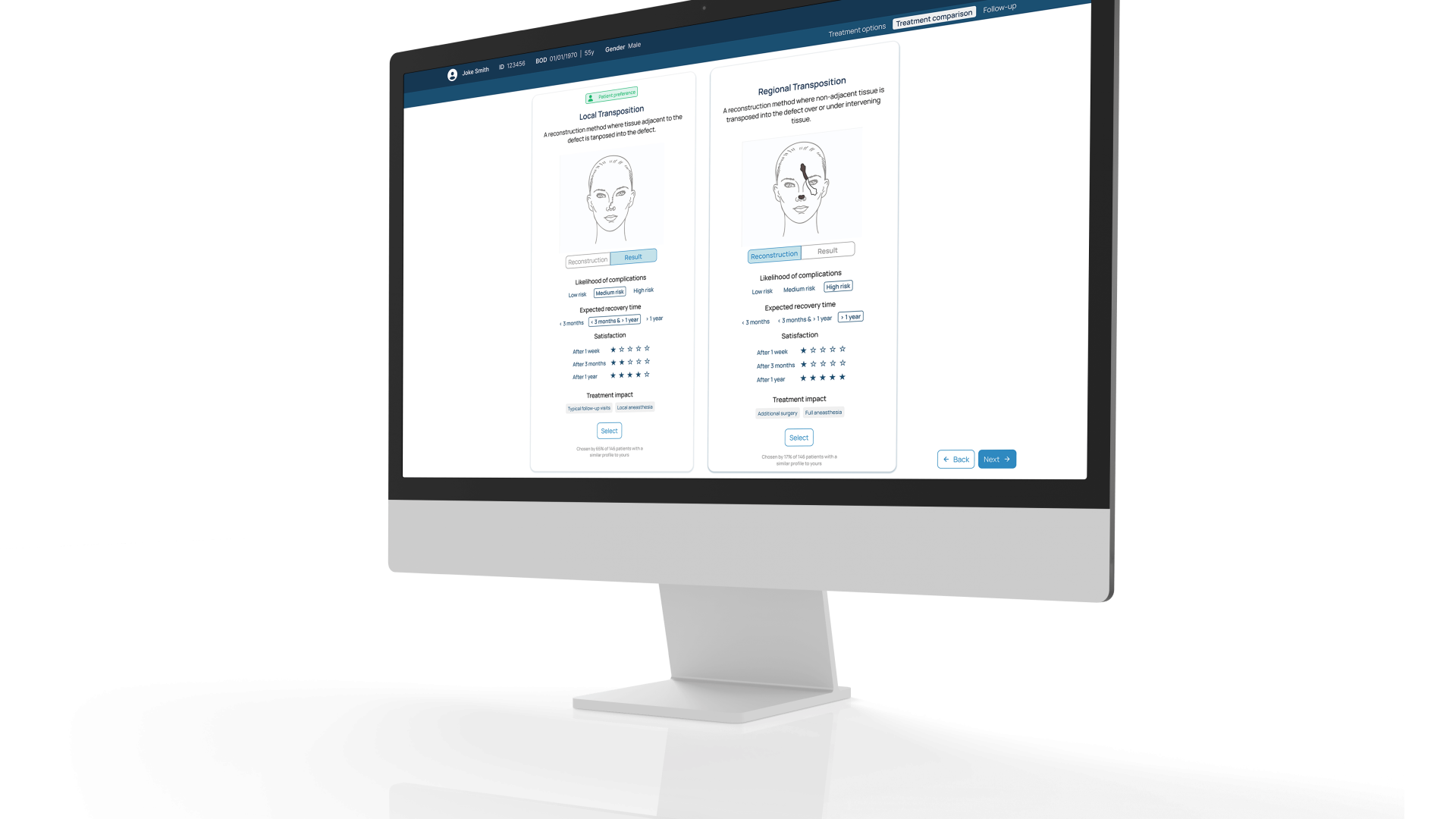
In this project, we explored how AI can help to align patient-physician communication and facilitate shared decision-making by redesigning the care pathway of nasal reconstruction after skin cancer removal.
Redesigning the care pathway
We approached the project holistically, combining Multilevel Service Design with Double Diamond innovation. By mapping patient-physician interactions, data flows, and technical systems, we were able to understand the entire process with accommodating pain points and needs. From here, we co-created a service solution with multiple stakeholders like clinicians, designers, and data experts.
The outcome is a predictive decision-support tool that matches patient profiles with past cases to forecast the most satisfying reconstruction option. the tool guides both patient and clinician preparation, standardizes a more patient-centered consultation, and is supported by a data strategy to enable data-informed care.
Human-centered AI
While AI holds great potential to personalise and enhance healthcare, it cannot operate effectively alone. Our work shows that predictive tools succeed only when people, processes, and systems adapt alongside them. Redesigning this care pathway also highlighted a bigger challenge: messy and fragmented healthcare data. We must collaborate toward a solid infrastructure before AI can make a real impact in healthcare.
 Free wifi available
Free wifi available
 Toilets available
Toilets available
 Fully wheelchair accessible
Fully wheelchair accessible
 Wheelchair friendly toilet available
Wheelchair friendly toilet available